数据库相关笔记②
SQL
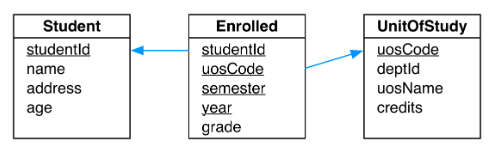
Introduction to SQL
SQL is a declarative language which means that you use it to describe what data you are interested in, but not how it should be retrieved. The database system uses a variety of algorithms internally to produce the query result. With declarative languages such as SQL, you do not need to worry about these implementation details.
Query
Your task is to write an SQL query. Your query must output the name and age of all students in the Student table.
select name,age from Student |
Select * from
The * (asterisk) wildcard is a useful shortcut when writing SQL queries. You can use the * wildcard in the SELECT clause to refer to a complete tuple of a table with all its attributes.
Your task is to write an SQL query. Your query must output all entries in the Student table and all available Student attributes.

select * from student |
WHERE Clause and Strings
Strings must be enclosed in single quotes (
'example').
Your task is to write an SQL query to output the result list for 'INFO2120', using data in the Enrolled table.
Your query’s result should have two columns:
- the
studentIdof each student who took INFO2120 at any point in time (ignore which year or semester the subject was taught); - the
gradethat student received for INFO2120.

select studentid,grade from enrolled where uosCode = 'INFO2120' |
COUNT
在 SQL 中,除了COUNT(*)函数外,其他的聚合函数如 SUM、AVG、MIN、MAX 在遇到 NULL 值时,会自动将 NULL 值忽略掉。
只有COUNT(*)不忽略 NULL
SELECT AVG(mark) FROM Assessments |
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Assessments |
SELECT COUNT(mark) FROM Assessments |
Distinct
SQL 中,count 函数如果不加 distinct 的话会计算重复的行数
SELECT COUNT(city) |
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT city) |
但这些聚合函数会去计算重复的 attribute,如果 unique 限制条件没有给出来的话
查找一共有多少学生注册
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Enrolled |
和这个是一样的
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT sid) FROM Enrolled |
找到 9120 最高分
SELECT MAX(mark) |
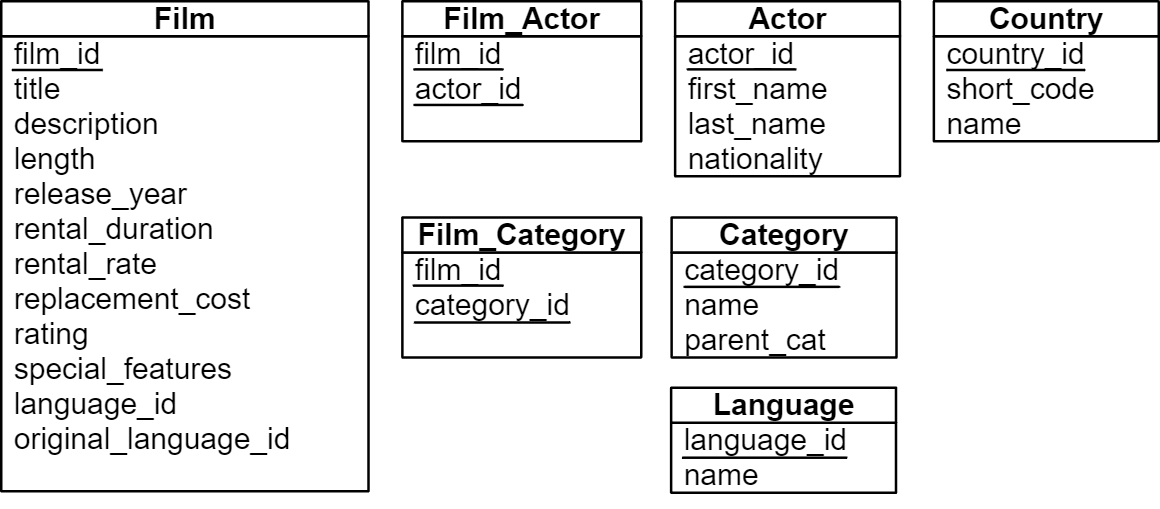
DDL (Data Definition Language)
CREATE TABLE
CREATE TABLE <tablename> ( |
Consistency Constraints
PRIMARY KEY
Declares an attribute (or several) as the unique identifier for rows in the table.
NOT NULL
Forces every row in the table to have a value for this attribute.
DEFAULT <default_value>
Specify a default value for an attribute.
Foreign Key Constraints
CREATE TABLE Film_Actor ( |
DROP TABLE
DROP TABLE <tablename>; |
Example
Write an SQL DDL statement that extends the DVD Shop database with an additional table for film studios, called Studio. Each Studio must have:
- a unique
studio_ididentifier (integer) - a
nameof up-to 50 characters length which must be given - an
address(up-to 100 chars long) - a specific
country(store the short code)
Make sure that the studio’scountryreferences theCountrytable. Bothcountryandnamemust always be stored for aStudio, but theaddressis optional.
create table Studio( |
DML (Data Manipulation Language)
INSERT
Used to insert a new row into a table.
INSERT INTO <tablename> VALUES (...); |
DELETE
Used to delete zero or more rows from a table.
DELETE FROM <tablename> WHERE <condition>; |
UPDATE
Used to update the content of zero or more rows in a table.
UPDATE <tablename> SET <expression> WHERE <condition>; |
Example

Add a new actor into the Actor table for 'Arnold Schwarzenegger' with ID 4711. Arnold is born in Austria.
insert into actor values(4711,'Arnold','Schwarzenegger','AT'); |
Update the database so that rental_rate of the Film 'ANGELS LIFE' is increased by 20%.
update film |
WHERE (Range Queries)
point queries
search for individual database entries, typically specified with an equality (=) condition.
range queries
select multiple rows in a defined value range.
| Operator | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| = | equal to | WHERE age = 20 |
| > | greater than | WHERE age > 20 |
| >= | greater than or equal | WHERE age >= 20 |
| < | smaller than | WHERE age < 20 |
| <= | smaller than or equal | WHERE age <= 20 |
| <> / != | unequal to | WHERE age != 20 |
| between | between start and end value (inclusive) | WHERE age between 20 and 25 |
| in | set of valid values | WHERE age in (20,21,22) |
ORDER BY
SELECT studentId, age |
``
DESC: Z-A 大到小
ASC: A-Z 小到大
DISTINCT
DISTINCT 关键字用于返回结果集中唯一不同的值。你可以在 SELECT 语句中使用它来消除重复的行。
虽然我们可以使用 DISTINCT 关键字删除结果中的重复项,但我们也可以使用 ALL 显式保留它们
LIKE
%matches any string of 0 to unlimited many characters_matches exactly one character
LIKE 'Database%'--以Database开头 |
注意默认情况下,SQL 的 LIKE 比较区分大小写
WHERE uosName LIKE '%systems%'; |
NULL Values
查询还没有成绩的学生
SELECT sid |
利用 IS NULL 或者 IS NOT NULL 可以在 SQL 中查找 nulI 值
任何包含 NULL 的算术表达式的结果为空,
如 3+NuII 还是 Null
任何比较符号如>,<等,和 Null 一起返回 Unknown
在 where 子句中,其会将 Unknown 认定为 false
SELECT sid |
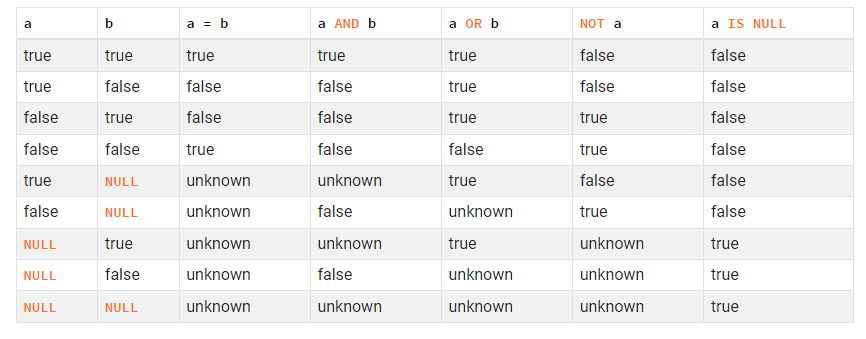
Three-valued logic for Boolean operations
这段内容是关于 SQL 中的三值逻辑(3VL)的。在 SQL 中,布尔值不仅可以是 TRUE 或 FALSE,还可以是 UNKNOWN。这主要是因为 SQL 需要处理 NULL 值,而 NULL 在 SQL 中表示未知或缺失的值。因此,当我们在 SQL 中进行逻辑运算时,需要考虑到 UNKNOWN 这种情况。
以下是对这段内容的详细解释:
-
OR运算:如果其中一个值为 TRUE,则结果为 TRUE,无论另一个值是什么。如果其中一个值为 FALSE,另一个值为 UNKNOWN,则结果为 UNKNOWN。如果两个值都为 UNKNOWN,则结果为 UNKNOWN。 -
AND运算:如果其中一个值为 FALSE,则结果为 FALSE,无论另一个值是什么。如果其中一个值为 TRUE,另一个值为 UNKNOWN,则结果为 UNKNOWN。如果两个值都为 UNKNOWN,则结果为 UNKNOWN。 -
NOT运算:如果值为 UNKNOWN,则结果仍为 UNKNOWN。因为我们不能确定未知值的非(NOT)是什么。
这就是为什么在 SQL 中,当我们处理包含 NULL 值的数据时,需要特别小心。因为 NULL 值会影响逻辑运算的结果。
- OR:
- (unknown OR true) = true
- (unknown OR false) = unknown
- (unknown OR unknown) = unknown
- AND:
- (true AND unknown) = unknown
- (false AND unknown) = false
- (unknown AND unknown) = unknown
- NOT:
- (NOT unknown) = unknown
SELECT * |
SELECT |
Making NULL Visible
\pset null '[NULL]' |
COALESCE Function
The COALESCE( expr , value_if_null ) function returns the second argument (value_if_null) if the expression in the first argument (expr) evaluates to NULL.
如果第一个参数 (expr) 中的表达式计算为 NULL ,则 COALESCE( expr , value_if_null ) 函数返回第二个参数 (value_if_null)
SELECT studentId, COALESCE(grade, '[UNKNOWN]') |
VIEW
The CREATE VIEW DDL statement extends the current database schema with a new view:
Views ≠ Tables
Existing views can be removed with the DROP VIEW command. The general syntax is:
DROP VIEW <viewname>; |
Your task is to write an SQL DDL statement which creates a new view called LengthyDramas. This view should list all 'drama' films (as mentioned in their description regardless of capitalisation) which have a running time over 90 minutes. Your view needs to have the following attributes:
id- thefilm_idof each dramatitle- thetitleof each dramayear- therelease_yearof each dramaminutes- thelengthof each drama
Your view also needs to list dramas in reverse order of their running time (minutes). Any dramas with the same running time should be further sorted in alphabetical order by theirtitle.

create view LengthyDramas as |
JOIN
Equi-Join
Your task is to write an SQL query that finds the number of actors who acted in the Film entitled 'ALONE TRIP'. Your query should return just the number of actors.

select count(actor_id) from |
Multiple Explicit Equi-Join
Your task is to write an SQL query that lists the title of every Film in which the Actor named JOHNNY CAGE has appeared. The titles should be in alphabetical order.
select A.title from |
Natural Join
Natural Join 两个表一定要有一个公共属性是一样的才行
Natural Join vs. Explicit Equi-Join

SELECT * |
SELECT * |
Multi-way Natural Joins
SELECT studentId, name |
Example
Your task is to write an SQL query that lists every Film in the Category 'Horror' that is rated 'R', in alphabetical order by title. Your query should return these attributes:
film_id;title; andrelease_year.
Try to make use of SQL’sNATURAL JOINoperator in your answer.

select film_id,title,release_year from |
Inner Join
r1 JOIN r2 ON ( condition )
r1 JOIN r2 USING ( field(s) )
SELECT year, name |
Further JOIN Examples
以下查询查找所有学分点数少于 info2120 的研究单位。
SELECT U2.uoscode, U2.credits |
SELECT U2.uoscode, U2.credits |
Using
SELECT name |
Examples

Your task is to write an SQL query that lists the first_name and last_name of every Actor who played in the Film entitled 'AMERICAN CIRCUS', in alphabetical order by last name. Try to use SQL’s INNER JOIN operator in your answer.
select first_name,last_name from |
Your task is to write an SQL query that lists all film sub-categories and their corresponding parent categories. Your query’s result should contain the following attributes:
category_id;category- the name of the category; andparent- the name of the category’s parent category.
You should ignore any category which does not have a parent category, i.e. your query’s result table should contain noNULLs.
select A.category_id, |
We are looking for the correct way to join two tables which have no attributes in common. The following query tries to find the Country name for the nationality of every Actor with last name 'DEPP':
SELECT first_name, last_name, |
SELECT first_name, last_name, |
Outer Joins
左外连接(LEFT OUTER JOIN)
左外连接(LEFT OUTER JOIN)返回左表中的所有行和右表中匹配的行。如果右表中没有匹配的行,则结果中的对应行将包含 NULL。
例如,我们有两个表,表 A 和表 B:
表 A:
| A_id | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | 张三 |
| 2 | 李四 |
| 3 | 王五 |
表 B:
| B_id | Name |
|---|---|
| 2 | 李四 |
| 3 | 王五 |
| 4 | 赵六 |
如果我们进行左外连接(以 Name 为连接条件),结果将如下:
SELECT * FROM A LEFT OUTER JOIN B ON A.Name = B.Name; |
结果:
| A_id | Name | B_id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 张三 | NULL |
| 2 | 李四 | 2 |
| 3 | 王五 | 3 |
右外连接(RIGHT OUTER JOIN)
右外连接(RIGHT OUTER JOIN)返回右表中的所有行和左表中匹配的行。如果左表中没有匹配的行,则结果中的对应行将包含 NULL。
如果我们进行右外连接(以 Name 为连接条件),结果将如下:
| A_id | Name | B_id |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 李四 | 2 |
| 3 | 王五 | 3 |
| NULL | 赵六 | 4 |
全外连接(FULL OUTER JOIN)
全外连接(FULL OUTER JOIN)返回左表和右表中的所有行。如果左表和右表中的行在连接条件上没有匹配,那么结果表中的对应行将包含 NULL。
如果我们进行全外连接(以 Name 为连接条件),结果将如下:
| A_id | Name | B_id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 张三 | NULL |
| 2 | 李四 | 2 |
| 3 | 王五 | 3 |
| NULL | 赵六 | 4 |
Examples
Your task is to write an SQL query to return the title of all films released in 2004 and all cast members (Actors) who played in those films. Your query should return the following columns:
- Title of the
Film; - First name of the
Actor, orN/Aif the film has no actors; and - Last name of the
Actor, orN/Aif the film has no actors.

select title, |
Set Operations
UNION
INTERSECT
EXCEPT
Examples
The set operators require that all input relations have the same schema. In other words, queries that are combined with either UNION, INTERSECT, or EXCEPT need to return their result in the same format.
The following query tries to identify all countries which have at least one actor named ‘DEPP’:

( |
( |
Duplicates in Set Results
By default, the set operations return results without duplicates. If you need to keep all input values, even if they occur multiple times in the result, you can use a set operation with the ALL keyword.
默认情况下,set 操作返回无重复项的结果。如果需要保留所有输入值,即使它们在结果中多次出现,也可以使用带有 ALL 关键字的设置操作。
The same ALL modifier is available to all set operators:
UNION ALLsee aboveINTERSECT ALLkeeps duplicates in intersectionsEXCEPT ALLkeeps duplicates after set difference
CROSS JOIN
笛卡尔积

Your task is to write an SQL query that finds all entries in the Actor table where the first_name and last_name are the same as another actor’s first and last names.

select A.actor_id,A.first_name,A.last_name |
Mathematical operators in SELECT
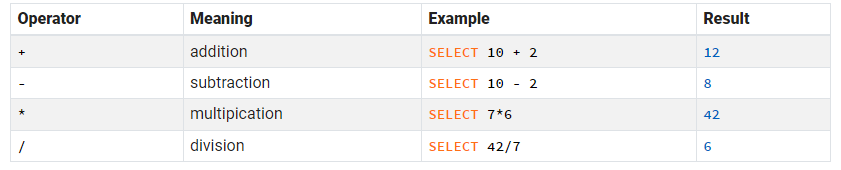
Select 子句中可以包含加减乘除
例子:
SELECT ID,title,Salary*2 FROM Staff |
SELECT ID,title,Salary-2000 FROM Staff |
SELECT ID,title,Salary/2 FROM Staff |
SELECT ID,title,Salary+2000 FROM Staff |
Mathematical functions in SQL
它们通常用在 SELECT 语句或 WHERE 子句中。这些函数包括:
mod(a, b):计算a除以b的余数。 示例:SELECT mod(10, 3);这将返回1,因为10除以3的余数是1。round(n, d):将数字n四舍五入到小数点后d位。 示例:SELECT round(3.14159, 2);这将返回3.14。trunc(n, d):将数字n截断到小数点后d位,不进行四舍五入。 示例:SELECT trunc(3.14159, 2);这将返回3.14。ceil(n):计算不小于n的最小整数值。 示例:SELECT ceil(3.1);这将返回4。floor(n):计算不大于n的最大整数值。 示例:SELECT floor(3.9);这将返回3。abs(n):计算数字n的绝对值。 示例:SELECT abs(-5);这将返回5。
Your task is to write an SQL query to calculate the length of every 'R'-rated Film in hours and minutes. Your query’s result must have the following columns:
film_idof theFilm;titleof theFilm;hours- length of theFilmin hours; andminutes- length of theFilmin minutes.

select |
String Operators in SELECT
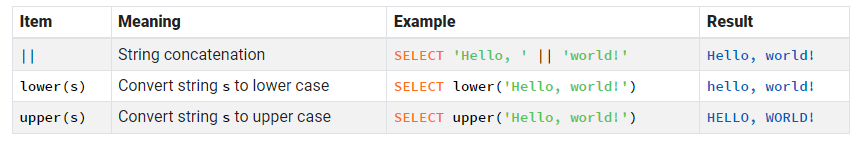
Your task is to write an SQL query to list the actor_id and fullname of every Actor whose last_name begins with 'A'. The name of each Actor should be given as a single value in the format
select actor_id,(last_name || ', ' || first_name) as fullname |
| actor_id | fullname |
|---|---|
| 58 | AKROYD, CHRISTIAN |
| 76 | ASTAIRE, ANGELINA |
| 92 | AKROYD, KIRSTEN |
| 118 | ALLEN, CUBA |
Nesting SQL Queries
找到成绩最高的学生
SELECT sid |
找到没有在 2020-s2 注册的学生姓名
SELECT name |
Co-related subqueries
相关子查询在执行过程中依赖于外部查询的每一行数据。简而言之,对于外部查询返回的每一行记录,相关子查询都会执行一次。
举个例子,如果你想查询每个部门薪资最高的员工,你可能会这样写:
SELECT employee_name, salary, department_id |
在这个查询中,外部查询遍历 employees 表中的每一行,对于每一个 department_id,子查询都会重新执行并找出该部门的最高薪资。因为子查询中的 e2.department_id = e1.department_id 这一条件,这是一个典型的相关子查询。
Non-co-related subqueries
非相关子查询与外部查询独立,它不依赖于外部查询的任何一行数据,也就是说它只执行一次,并且结果通常被外部查询整体使用。
例如,你可以查询所有薪资高于公司平均薪资的员工:
SELECT employee_name, salary |
比较
- 性能:因为相关子查询可能需要对外部查询的每一行都执行一次,所以通常比非相关子查询慢。优化器可能难以对相关子查询进行优化。
- 使用场景:相关子查询适合于需要基于外部查询每行数据进行评估的情况。而非相关子查询适合于可以独立计算一次,然后应用于所有外部查询行的情况。
- 复杂性:相关子查询通常逻辑更加复杂,因为它们必须考虑与外部查询的关系。
EXISTS
EXISTS 用于测试子查询是否返回至少一行数据。如果子查询返回至少一行,那么 EXISTS 的条件为真(TRUE),整个 WHERE 子句的条件也就为真。EXISTS 常用于相关子查询,因为它们允许子查询引用外部查询中的列。
举个例子,假设你有一个订单表(orders)和一个订单明细表(order_details),现在你想找出至少有一条订单明细的所有订单:
SELECT order_id, customer_id |
在这个例子中,EXISTS 子查询检查 order_details 表中是否有与外部查询中 orders 表的 order_id 相匹配的行。如果有,返回这个 order_id 的订单。
与 EXISTS 相反,NOT EXISTS 用于测试子查询是否返回零行。如果子查询没有返回任何行,那么 NOT EXISTS 的条件为真。NOT EXISTS 通常用于排除在其他关联表中有相关记录的行。
继续使用上面的例子,如果你想找出没有任何订单明细的订单,你可以这样写:
SELECT order_id, customer_id |
在这个例子中,NOT EXISTS 子查询检查 order_details 表中是否有与 orders 表的 order_id 相匹配的行。如果没有,说明这个订单没有任何订单明细,那么就返回这个 order_id 的订单。
使用场景
- 当你需要确认至少存在一条符合特定条件的记录时,使用
EXISTS。 - 当你需要确认不存在任何符合特定条件的记录时,使用
NOT EXISTS。
Grouping
语法结构
SELECT column_name(s) |
此 SQL 查询用于从表中检索数据并根据指定的条件对其进行分组和排序。
- SELECT 子句指定要从表中选择的列。
- FROM 子句指定要查询的表。
- WHERE 子句指定要应用于返回结果的条件。
- GROUP BY 子句指定要分组的列。
- ORDER BY 子句指定要排序的列以及排序顺序(升序或降序)。
| company | amount |
|---|---|
| IBM | 5000 |
| DELL | 4500 |
| IBM | 7000 |
SELECT company, SUM(amount) |
| company | amount |
|---|---|
| IBM | 12000 |
| DELL | 4500 |
Having
Having 子句可以进一步筛选 group
SELECT uos_code, AVG(mark) |
SELECT country |
查找所有学生人数超过 1 人的 6 个学分点课程的学生总人数
SELECT e.uos_code, COUNT(*) |
DCL (Data Control Language)
Commands that control a database, including administering privileges and users


Example5
- Which lecturers (by id and name) have taught both ‘INFO2120’ and ‘INFO3404’? Write a SQL query to answer this question using a SET operator.哪些讲师(按 ID 和姓名)同时讲授过 "INFO2120 "和 “INFO3404”?使用 SET 操作符编写一个 SQL 查询来回答这个问题。
SELECT id, name |
- Which lecturers (by id and name) have taught both ‘INFO2120’ and ‘INFO3404’? Answer this using a sub-query without SET operators. Make sure your result doesn’t include duplicates.哪些讲师(按 ID 和姓名)同时讲授过 "INFO2120 "和 “INFO3404”?使用不含 SET 操作符的子查询回答此问题。确保您的结果不包括重复结果。
SELECT DISTINCT id, name |
- Write a SQL query to give the student IDs of all students who have enrolled in only one lecture using GROUP BY, and order the result by student ID. A lecture is a unit_of_study in a semester of a year.编写一条 SQL 查询,使用 GROUP BY 列出所有只参加过一次讲座的学生的学号,并按学号对结果排序。讲座是一年中一个学期的一个学习单元。
SELECT studId FROM Transcript |


